The goal of this master class is to create expansion packs for the Lego Mindstorms NXT product. The student follow a series of lectures on the underlying technologies and in the end design and build their extension pack.
Water Pump
Tom van Bergen
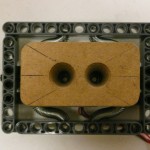
Tom created a Lego water pump that is based on the Kavan 0190 pump (12V). He build a casing using a 3D rapid prototyping (SLS) machine. The pump’s two electronic connection points (positive and negative DC poles) were soldered directly to an NXT plug from Mindsensors, allowing the pump to be run forwards and backwards using PWM signals. The pump can be controlled in the same way as an old fashion DC LEGO motor. A benchmark test with the NXT showed the pump can push ~0.9 liter per minute at full power.
GPS Sensor
Martijn ten Bhömer
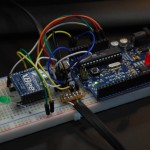
Martijn developed a GPS sensor that connects to the NXT with a cable using an intermediary micro controller. He used the NMEA-0183 standard to communicate between the USGlobalSat EM-406A GPS sensor and the micro controller. The micro controller then communicates with the NXT using the I2C protocol. In essence, the NXT is connected to the GPS sensor with a bi-directional communication.
Project report Martijn ten Bhomer
Wireless Sensor Bridge
Tom Frissen
Tom build a wireless bridge between sensors and the NXT. The NXT is already able to communicate using Bluetooth, but naturally, the Bluetooth communication is limited to several meters. Tom used the XBee modules to enable communication between sensors and the NXT over more than 1km.
Optical Mouse Sensor
Martijn Jansen
Martijn connect and optical mouse to the NXT using an intermediary micro controller. The system allows the NXT to read the coordinates of the optical mouse sensor. This is particularly useful for determining the position of mobile robots.
Magnetic Grabber
Eelco Klaver
Elco used a magnetic latching solenoid to build a magnetic grabber. The solenoid used is designed for low duty cycle applications where the solenoid’s energized position is needed for an extended period of time. The plunger latches magnetically in his basic position, until a negative electrical pulse is applied to allow the plunger to unlatch. Elco also build a mechanical guiding system to allow the plunger to reliable enter the hole of the solenoid.














Hi from Vancouver BC,
I am interested in learning more about how Martijn ten Bhömer developed his GPS sensor. I’d really like to do the same thing with my Mindstorms. Can you put us in touch?
Thanks,
Chris
I am going to build these devices (when I have time and have fully read your instructions), and I also have some suggestions. For example, could you create a wireless motor bridge (like the sensor bridge, but for motors; perfect for the tangled cords to the other side of a turntable situation); or an operating system using the optical mouse sensor and/or keyboard (seen on this site: http://www.extremenxt.com/keyboard.html)? It could also be interesting to have the NXT program itself or control USB devices through its USB port.
Hoping for more sensors,
NNG
Where are the schematics? Or the page where these can be purchased? And where do I find the technology used to make a case to the hardware? My E-mail is NickNackGus@gmail.com, and I am interested in all of the tools shown here. (It might be cool to build a mobile robot, attach a robot arm, and have the arm attach different tools using the magnetic grabber, the wireless sensor bridge, and some IIC devices…or maybe a special type of connector…or just a split wire that connects with the attachment of a tool…)